Basic Git & GitHub Workflows
This page provides essential workflows for managing your projects with Git and GitHub on the HiPerGator system, focusing on advanced techniques like forking, synchronizing, and creating pull requests. It aims to streamline your experience with the complex Git workflows on HiPerGator, helping you manage your projects efficiently and collaboratively.
Forking a Repository and Setting Up Local and HiPerGator Repositories
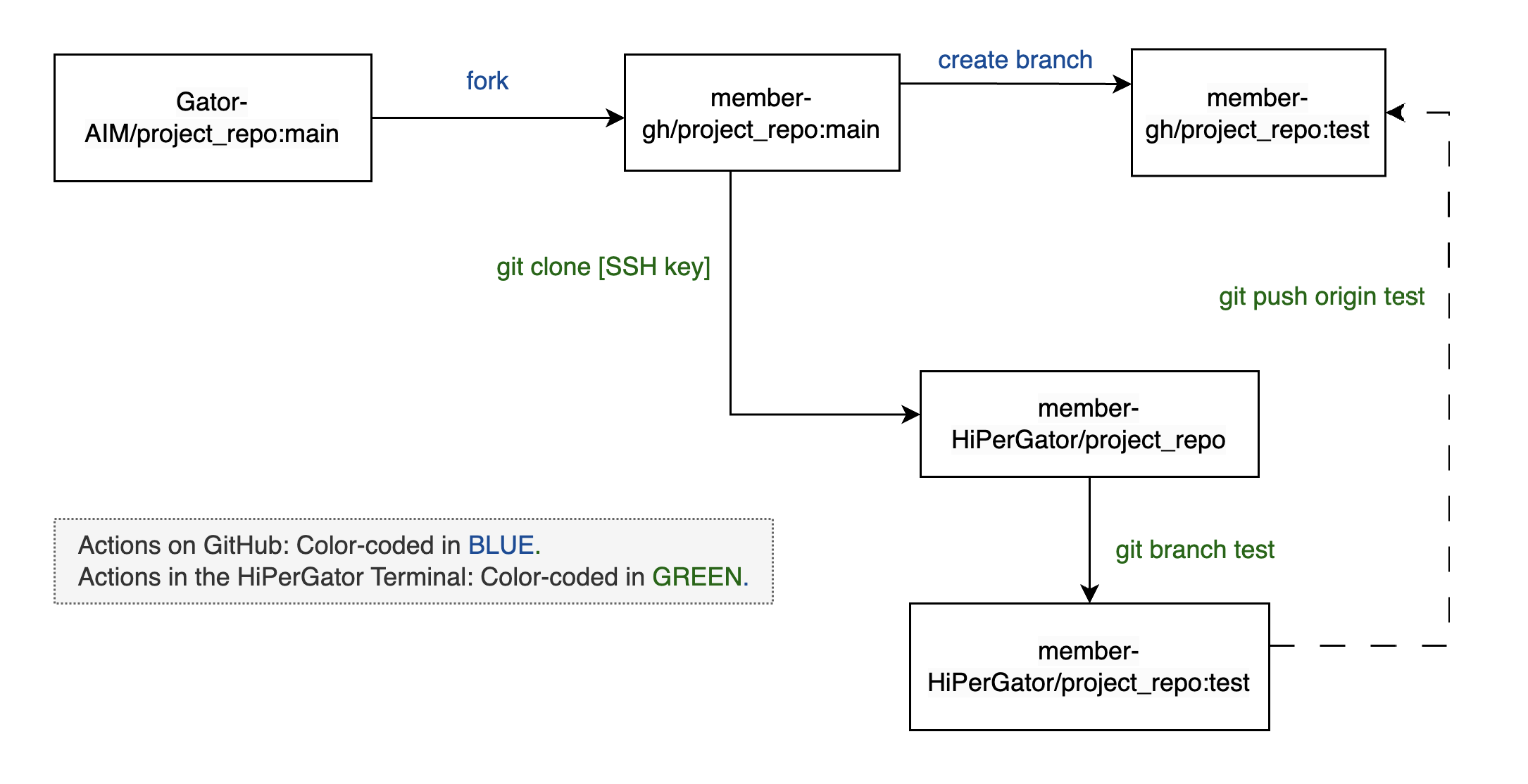
This is the process of creating a personal copy of a shared lab repository, and then cloning this fork to both your local machine and the HiPerGator environment. It includes steps for creating a new branch for your specific changes and pushing this branch to GitHub to ensure all changes are synchronized and tracked.
- Fork the Repository:
- Navigate to the lab repository (e.g.,
Gator-AIM/project_repo) on our lab’s GitHub account. Ensure you are logged into your GitHub account and use the Fork button to create a copy under your account (e.g.,member-gh/project_repo).
- Navigate to the lab repository (e.g.,
- Clone the Repository:
- Log in to the terminal on your local machine or HiPerGator. Ensure your SSH keys are set up for GitHub, then use SSH to clone the repository into both your local and HiPerGator environments:
git clone git@github.com:member-gh/project_repo.git
- Log in to the terminal on your local machine or HiPerGator. Ensure your SSH keys are set up for GitHub, then use SSH to clone the repository into both your local and HiPerGator environments:
- Create and Checkout a Branch:
- In your local repository, create a new branch named
testfor making changes and switch to it using:git checkout -b test
- In your local repository, create a new branch named
- Push the New Branch:
- Push the local
testbranch to the correspondingtestbranch on the forked GitHub repository for remote tracking. If thetestbranch does not exist on GitHub, create it first:git push origin test
- Push the local
The workflow is illustrated in Figure 1 below.
Synchronizing the Fork with the Upstream Repository
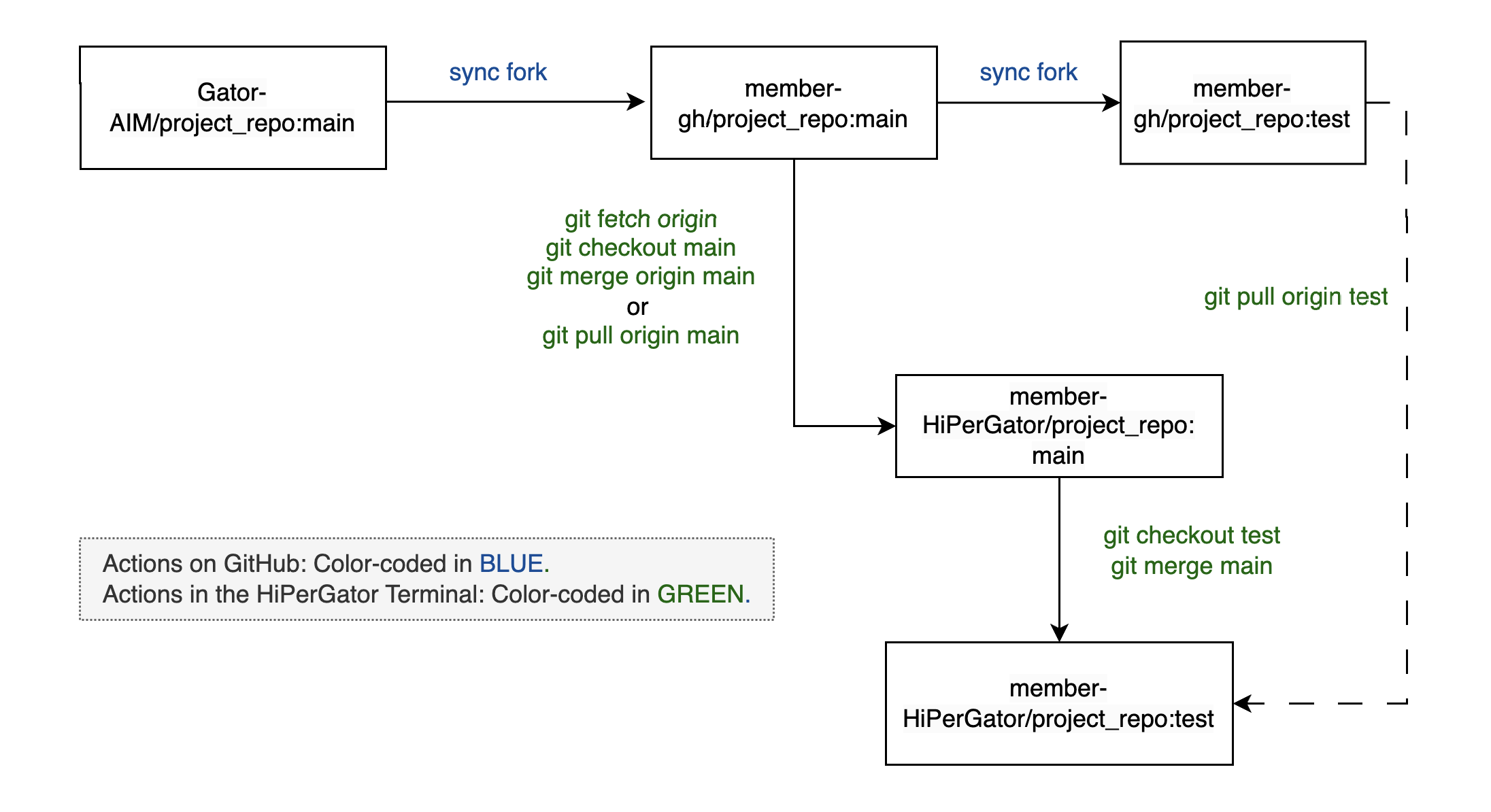
This workflow is critical for keeping your fork up-to-date with the original repository (often called the upstream repository). It involves fetching updates from the upstream, merging them into your local main branch, and updating any development branches with these changes to ensure consistency and prevent conflicts.
- Sync Fork on GitHub: Navigate to your fork on GitHub. Click the
Sync forkbutton to pull in the latest changes from the upstream (lab) repository into your fork. This action synchronizes your fork’s main branch with the upstream main branch without needing to use local Git commands. - Fetch and Merge Changes from Your Synced Fork:
- Ensure you are on the
mainbranch in your local repo by running the following command in your local or HiPerGator terminal:git checkout main - Fetch the latest changes from your GitHub fork and merge them into your local
mainbranch with:git fetch origin git merge origin main - Alternatively, you can combine these two steps by running the
git pullcommand directly:git pull origin main
- Ensure you are on the
- Update Your Feature Branch:
- Switch to your
testbranch and merge the changes from the updatedmainbranch to keep it current:git checkout test git merge main
- Switch to your
The workflow is illustrated in Figure 2 below.
Committing Changes and Creating Pull Requests to the Upstream Repository
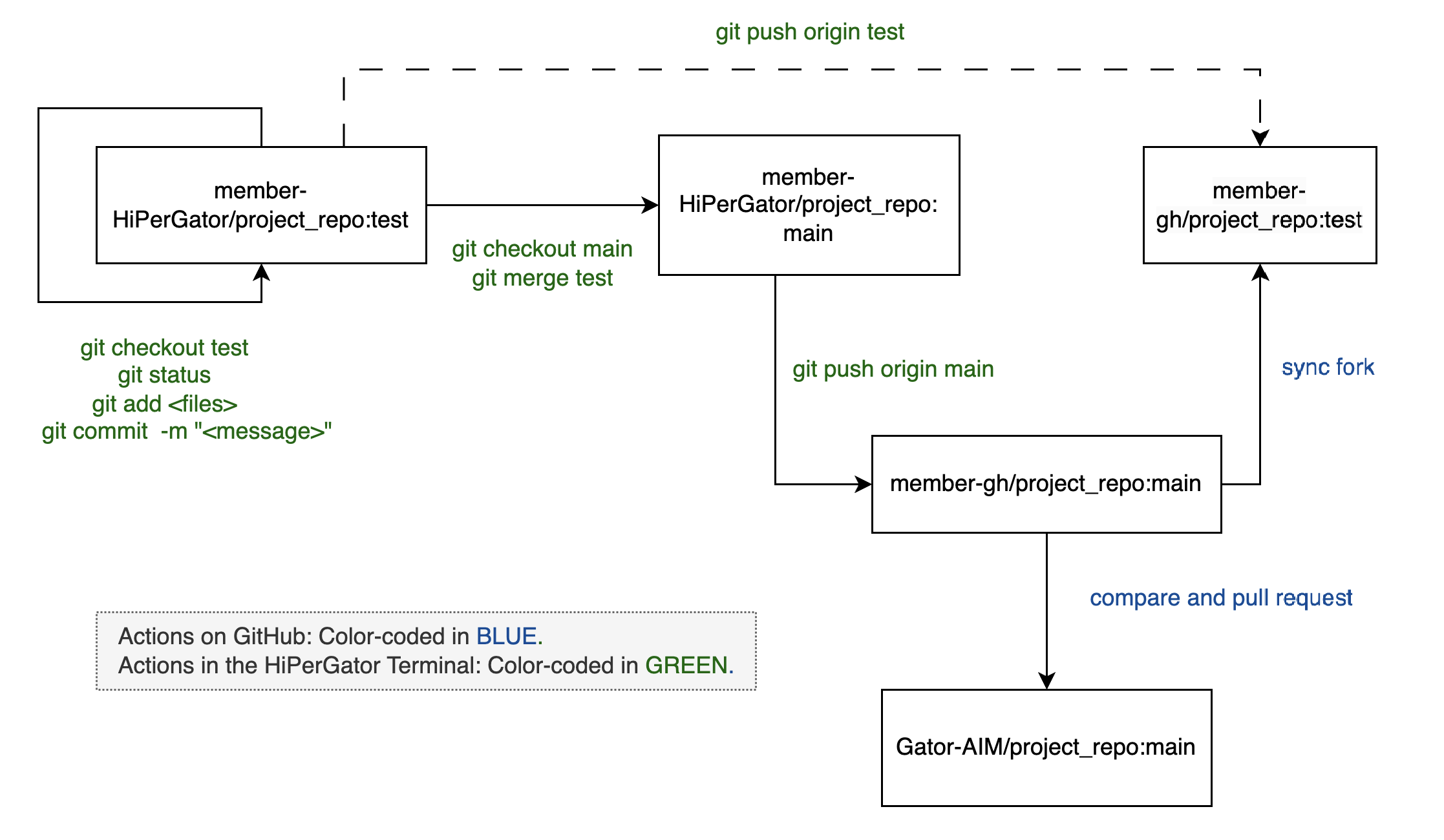
The following are the steps to make and commit changes locally, push these changes to forked repository on the member’s personal GitHub account, and then create a pull request to merge these changes back to the shared project repository in the lab GitHub. This is essential for contributing your updates back to the project and collaborating with other contributors.
- Commit Changes Locally:
- Switch to your local
testbranch, check the status, stage the changes, and commit them by running the following commands in your local/HiPerGator terminal:git checkout test git add <file_names> git commit -m "Describe changes here" - After committing on
test, switch to themainbranch in your local repository and merge the changes fromtest:git checkout main git merge test
- Switch to your local
- Push Local Changes to the Forked Repo:
- Push changes from your local
mainbranch to themainbranch on your fork on GitHub with:git push origin main - Similarly, update the
testbranch on your fork with:git push origin test
- Push changes from your local
- Create a Pull Request:
- Go to your fork on GitHub and select the
Compare & pull requestbutton to initiate a pull request to the upstreammainbranch of the lab repository. - Before creating the pull request, review and, if necessary, rebase or update your branch. This is particularly important if the upstream main branch has been updated since your fork was last synchronized. This helps to ensure that your changes can be merged smoothly.
- Go to your fork on GitHub and select the
The workflow is illustrated in Figure 3 below.
In Summary
The workflows detailed above for forking a repository, synchronizing with the upstream, and committing changes to create pull requests are integral to managing projects efficiently within our lab. These procedures are designed to ensure that all team members can contribute to our repositories in a structured and secure manner, while maintaining the integrity and consistency of the lab’s projects.
By centralizing the creation of repositories to the lab GitHub administrator, we ensure that all projects start with the correct setup. Team members then fork these established repositories to their personal accounts to work independently. This allows for innovation and individual contributions without risking the stability of the main project. Changes are then carefully merged back into the main repository through pull requests, which are thoroughly reviewed to maintain high standards.
This systematic approach minimizes conflicts and ensures that contributions align with our project goals and quality standards, fostering a collaborative and productive research environment.